You know what they say: everything old is new brewed again.
At least that’s true when it comes to fermentation, that ancient food and beverage production process that is currently an overnight sensation. It is going well beyond the time-honored probiotic-rich staples of sauerkraut, kefir, pickles, miso, yogurt, and kombucha. The process of fermentation is being utilized in the creation of alternative, sustainable proteins to take the place of meat, eggs, seafood, and dairy. And it’s projected to get even more significant in its scope and revenue.
Data in The Good Food Institute’s 2021 State of Fermentation Industry Report points to the growth of fermentation as a traditional means to create probiotic-rich foods and plant-based products. According to the report, a total of $1.69 billion was invested in 54 fermentation-based startups in 2021.
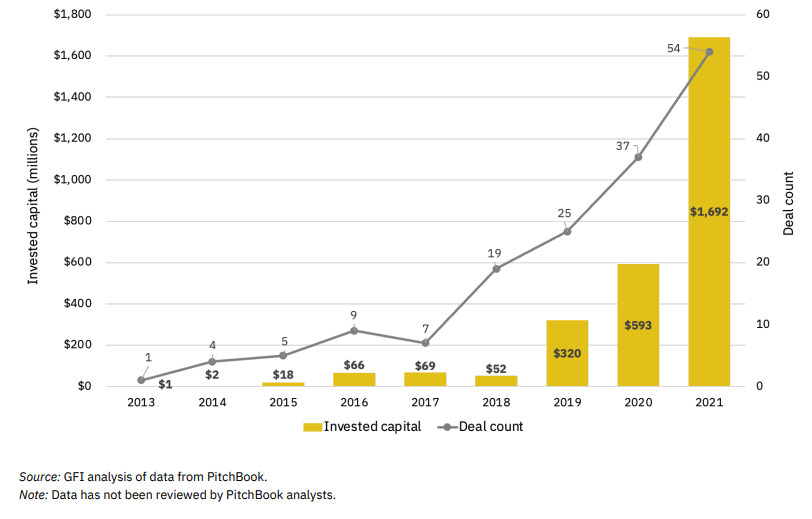
Other data from GFI’s report:
- Fifteen known startups dedicated to fermentation for alternative proteins were founded in 2021, along with new suppliers focused on fermentation-enabled alternative protein ingredients.
- Eighty-eight known companies are now dedicated to fermentation-enabled alternative proteins, increasing 20 percent from the number of known companies in 2020.
- 2021 saw the first growth-stage fundraising in the fermentation industry, including three deals >$200 million.
It’s important to understand that fermentation is not a single process but is three separate processes. Traditional fermentation (used to make pickles, kombucha, and sauerkraut) uses live organisms (such as the fungus Rhizopus to make tempeh or a SCOBY to brew kombucha) to modulate ingredients to create a product rich in flavor and texture. One established company, Miyoko’s Creamery, uses fermentation to make its line of alternative protein dairy products.
A second process, biomass fermentation, takes advantage of the properties of certain microorganisms that quickly create large quantities of protein. The resulting protein can be used as a standalone product or an ingredient, which is the focus of most companies in this area. An example of a company employing biomass fermentation is SACCHA, a German company using spent brewer’s yeast to create an alternative vitamin-rich protein that can be used to develop animal-free metal. Colorado-based Meati Foods uses mycelium (a mushroom root) to create a fibrous material that resembles meat.
Precision fermentation, the third method, is perhaps the segment in this area with tremendous potential and is a focus of major investments. In precision fermentation, microbes create “cell factories” to build specific functional ingredients. Precision fermentation can produce enzymes, flavoring agents, proteins, vitamins, natural pigments, and fats. EVERY Company is an example of this process in which precision fermentation creates a substitute for traditional egg whites.
The GFI chart below shows the different types of fermentation as they relate to alternative proteins and highlights different possible products enabled by each.

One of the most significant stumbling blocks for the more advanced fermentation methods is the buildout of large-scale facilities to tackle production. A growing number of companies are in the process of recently completing or midst such construction, which points to 2023 as a timeframe in which production could begin to fulfill a growing market.
GFI’s report points to these as examples of completed projects and ones in the process of buildout:
- The Protein Brewery, Netherlands, completed 2021
- The Better Meat Co., California, completed in 2021
- Nature’s Fynd, Chicago, targeted for 2022-2023
- Mycorena. Sweden, expected to be completed in 2022
- Solar Foods, Finland, to be completed in 2022
With all the noise about the more advanced forms of fermentation, the value and growth of products in the “traditional fermentation” space have been overlooked. The kombucha market has skyrocketed with a focus on health, especially during the COVID-19 scare. According to Absolute Reports, the global Kombucha market size is estimated to be worth $2.1 billion in 2022 and is forecast to be $6.1 billion by 2028, with a CAGR of 19.7%.
And an old fermented standby, sauerkraut, also brings in big dollars. According to Verified Market Research, the sauerkraut market was valued at $8.7 billion in 2019 and is projected to reach $14.1 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 5.74% from 2020 to 2027.


















